Future Fabulators
Table of Contents
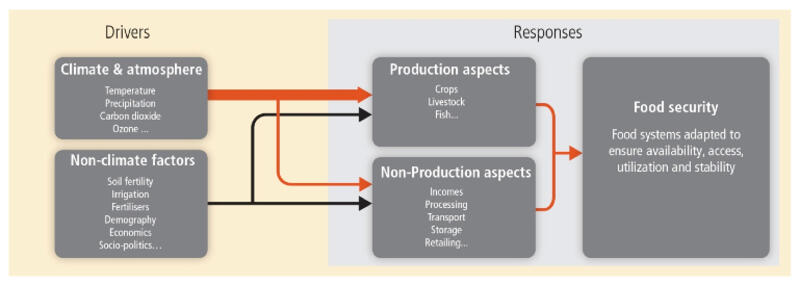
Food Horizons
On this page we collect drivers of change and horizon scanning notes, related to food, health and wellness. This is a preliminary step in the design of food scenarios, that we then translated into a tasting menu for Latelab Open Sauces at the Edinburgh Science Festival.
See the whole design process on the food futures page.
Current situation
(looking back from 50-100 years to today, focusing on problems and possibilities)
- hygiene, pasteurisation and the (anti)bacterial movement (better understanding of pathogens, pesticides, antibiotics and the rising dangers of antibiotic resistance)
- industrialisation of food production, focus on efficiency and feeding more people; less focus on taste, more on nutrition
- increased use of sugar, fat and meat (1995 the first deep-fried mars bar in Scotland)
- proliferation of cold chain transport - larger volume and longer distances (allowing for delocalisation and specialisation of production), availability of a wide range of products
- consumption patterns are changing: USA influence, food from around the world, seasonal flattening; food consumption moves from social to functional
- disposal: city scale, burned rather than composted
- wide spread of (bio-accumulative) toxins (packaging, hormones, slow-acting poisons, also in organic farming)
- the battle between bacteria and chemicals (and people who prefer one or the other)
- complex food distribution and production (present: focus on reduction of complexity and shortening of supply-chains)
- growing awareness of health risks
- present: refocusing on the local, respecialisation, relocalisation, bringing back forgotten varieties and species, focus on (hyper)seasonal products
- vicious circle of more people - more food: focus on cheap and voluminous rather than nutritious; lowering of household's food budgets - health risks due to consumption of junk food
- dangerous footprint of meat production (concentration of animal manure) and other industrial byproducts
- internet is changing distribution and consumption patterns, as well as non-industrial food production; information spreads faster and supply-chains are becoming more convoluted and personalised
- proliferation of foodies movements focused on healthy, tasty, virtuoso food preparation and consumption;
- open source food movements
- diet cults (and disconnection from food production and waste)
drivers
Social
- Health
- Diet
- Aging
- Urbanisation
- Food Culture
Technological
- Agricultural Technology
- GMO / Synthetic biology
- Internet of Things
- Customisation
- Antibiotic availability
- Food science
Economic
- Energy
- Financing
- Equality
- Dominant crops
- Scale
- Patenting
Environment
- Pollution
- Unpredictability
- Degradation
- Availability of raw materials (water, seeds, soil…)
Political
- Conservatism
- Nationalism
- Unconditional Basic Income
- Food Security
- Transnational Agreements
- Laws and Regulations
Thematically clustered drivers:



causal layered analysis
Analysis of thematically clustered drivers looking at their social causes, underlying worldviews and cultural myths:



Drivers in detail
Horizon: less than 50 years.
Technological
- Development of “resource-efficient” large-scale agriculture techniques (agro-ecological systems using bio-sourced fertilizers, methanisation…) (in french), article on Reporterre on French government's strategy towards "industrial agro-ecology"
- > adverse environmental impacts such as pollution & reduction in biodiversity (in French), article on Reporterre on adverse environmental effects of large-scale methanisation
- Development of GMO technology > combined with increased globalization of economy (see Economical trends), increase of GMO-food & GMO-seeds market share (in French), article on how the US-EU free-trade zone will bring GMO food to Europe
- > unknown health effects
- Existing minority, stable or decreasing, of small-scale sustainable farmers (promoted by Right-to-Food special rapporteur Olivier de Schutter) > preserving bio- and techno-diversity > increasing resilience to environmental crisis negative effects and mitigating the risk of such effects.
- Appearance of luxury technofood (like the lab-grown hamburger)
- > only for very rich people, with unknown impact on health.
Environmental
- Increasing pollution of water, soil and atmosphere
- > increasing systemic diseases such as cancer & neurodegenerative medicines
- > potentially contributing to a loss in biodiversity.
- Decrease of soil fertility > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food > starvation for specific locations & poor people; adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population; geopolitical instability.
- Changes in desertification and rainfall patterns > decrease of available arable soil surface > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food > starvation for specific locations & poor people, adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population; geopolitical instability.
- Climate change
- Increase of Extreme Climatic Events, e.g. Floods & Droughts
- > localized food scarcity;
- > when combined with hyper-specialization of food crops per location (see Economic trends), world-wide scarcity of specific ingredients.
- Change in seasonal patterns and average climatic conditions > change of food crops production balance worldwide.
- See detailed results from IPCC report below.
- Decrease of Biodiversity > decrease of edible animal & plant species > reduced resilience to change in seasonal patterns & climatic conditions > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population
- > geopolitical instability.
- Decrease of available energetic resources > Increase on “traveling food” prices > when combined with increased inequities in personal wealth (see Economical Ttrends), reduce of food ingredients availability for most of the population > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population
- > geopolitical instability.
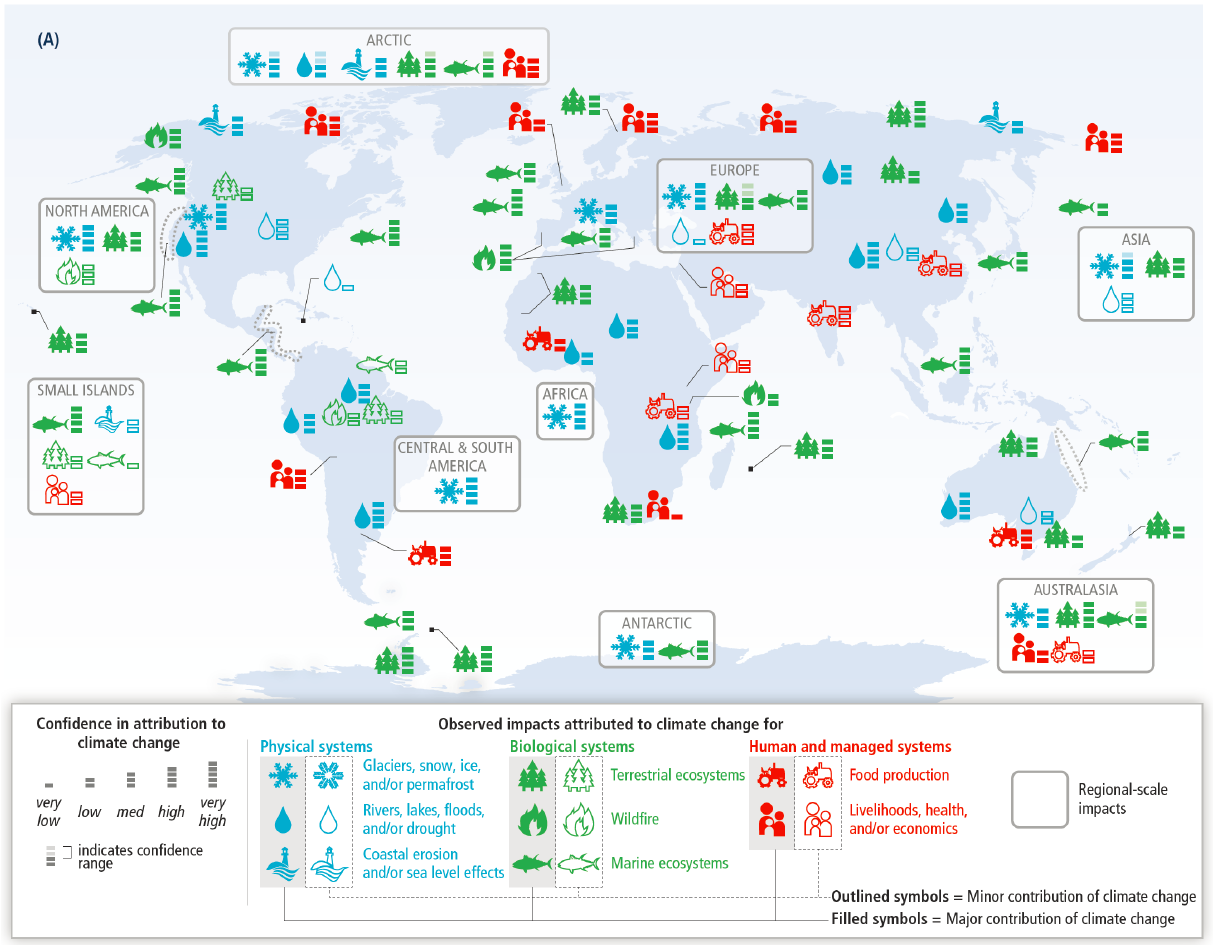
reference: IPCC WGII AR5 Chapter 7 “Food Security and Food Production Systems” http://ipcc-wg2.gov/AR5/images/uploads/WGIIAR5-Chap7_FGDall.pdf
IPCC AR5 WG2 Figure SPM.2a
Change in Plant Crops Production
- India: global loss in cereal production.
- Brazil: loss in cereal, drastic increase in beans.
- US: no big change in cerelas, slight increase in Soy
- Europe:
- Increase in plant crops in Boreal, Alpine, North & Central Atlantic & South Continental climates.
- Moderate change in Continental North.
- Decrease in Atlantic South & Mediterranean climates.
- Australia: global decrease.
Change in Livestock Production
- Africa: less Livestock & Dairy
- Europe:
- France: no impact on dairy yield, but impact both positive and negative + instability on forage fields.
- Italy & Netherlands: bad for mozzarella & gouda
- Disease increase: Bluetongue virus
- Oceania: decrease everywhere but South Australia.
- South America:
- Andean mountains: decrease of every livestock but sheep, which increase.
- Argentina & Chile: more beef cattle.
- Columbia, Venezuela & Ecuador: less beef cattle.
- North America: strong decrease of Dairy yields.
Economic
- Increased globalization of economy
- Prevalence of large-scale over small-scale food production > environmental impacts such as pollution & reduction of soil fertility > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food + most of the food heavily polluted
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people;
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population;
- > geopolitical instability.
- Hyper-specialisation of food crops grown on a given territory > reduced resilience to extreme climatic events (see Environmental trends) > potentially massive scarcity of a essential food crops > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food + most of the food heavily polluted
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people;
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population;
- > geopolitical instability.
- Increased financiarisation of economy
- Adverse effects of speculation on food prices > combined with increasing inequities in personal wealth, reduction of food availability and diversity for most of the world population > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people;
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population;
- > geopolitical instability.
- Increasing inequities in personal wealth > reduction of food availability and diversity for most of the world population > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population
- > geopolitical instability.
- To a minor extent, localized alternative economies, such as (in French) integral cooperatives, local currencies, barter networks & gift economy initiatives
- > reduces inequities within economic players at local scale
- > better global health at local population scale.
- Global game changer: if a major demographic group, global economic player & industrial producer installs basic income. It is about to be voted by the population in Switzerland and has been proposed as a popular initiative in Europe
- > depending on how it would be defined, it may reverse the large-scale industrial dynamics and may induced better global health & wellness results.
Social & Cultural
- Increase of global population > more food needed > combined with reduction of soil availability & fertility, reduction of available quantity & diversity of food + food heavily polluted or low in nutrients > starvation for specific locations & poor people; adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population; geopolitical instability.
- Increase of urban population
- Massive amount of energy used to bring food to urban citizens
- > increase energetic resource depletion rate (also needed for industrial food production) > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population
- > geopolitical instability.
- > increase of atmospheric, water and soil pollution due to massive transport
- > adverse health effects.
- Increased urban pressure on neighboring fertile soils > Reducing availability of fertile soils > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population
- > geopolitical instability.
- Prevalent cultural preference to industrially-produced food (Nestlé, McDonalds, Pizza Hut, Exki…)
- > existing demand stimulates production & thus industrial agriculture
- > pollution
- > adverse health effects
- > low food diversity
- > adverse health effects
- Most prevalent religions & related food regimes (Pork-free Islam & Bee-free hinduism ?)
- > changing the demand thus the production balance of food crops at world scale ?
- Minority, stable or increasing, adhering to the GASAPs, Slow Food & Organic Food movements > combined with participation to alternative economic systems (see Economical trends), localized positive impacts on available food diversity & global health.
Political
- Increase of patenting & decrease of authorized crop varieties (in French), an article from Mediapart on seeds patenting
- > reduction of animal & plant species available for cooking > global impoverishment of food culture.
- > decreased resilience to change in seasonal patterns & average climatic conditions > reduction of available quantity & diversity of food
- > starvation for specific locations & poor people
- > adverse health effects for a wide range of the world population
- > geopolitical instability.
- Increase of far-right, nationalist and identity-focused movements (in French), an article from les Inrocks analysing the situation of far-right parties in Europe > (violent) incentive back to traditional culture, and therefore cooking > reduction of food ingredients diversity at local scale ?
misc/notes/sort
“People tend to find the taste of Soylent to be familiar: the predominant sensation is one of doughiness. The liquid is smooth but grainy in your mouth, and it has a yeasty, comforting blandness about it.” Could Soylent Replace Food?
- Several food experts on food futures: http://time.com/3482452/future-of-food/
- infographics from foodnetwork http://www.wired.com/design/2013/10/26-amazing-food-infographics/
- historical changes in ingredients http://cryptoforest.blogspot.be/2013/11/charting-geographical-origins-of.html
- “The Honeywell Kitchen Computer or H316 […] represented the first time a computer was offered as a consumer product.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Honeywell_316#Kitchen_Computer
- “Bullipedia is a professional tool based on the codification of a creative discipline.” from elBulli Foundation. http://hackingbullipedia.org/bullipedia3-2
- “A Work in Progress: Notes on Food, Cooking and Creativity” by René Redzepi. http://nyjournalofbooks.com/review/work-progress-notes-food-cooking-and-creativity
- “TASTED is a project that investigates the way we taste food and its flavor.” http://www.simona-derosa.com/works/#/tasted/
- network analysis “Flavor network and the principles of food pairing”. http://www.nature.com/srep/2011/111215/srep00196/full/srep00196.html
- general principles of cooking with coconut milk. http://ask.metafilter.com/257507/What-are-the-general-principles-for-cooking-with-coconut-milk
- An app for flavour profiling. https://www.gastrograph.com/